MELPe - enhanced MELP
The MELPe codec can transcode its bitstream directly to another rate.
Suitable for band limited or efficiency limited communication systems such as satellite links and military applications.

MELP DoD standard specifies a 2400 bps mode of operation
MELPe is a triple-rate low codec that supports rates of 600 bps, 1200 bps, and 2400 bps
MELP: Overview
MELP (Multi-Excited-Linear-Prediction) is a voice compression codec originally developed for and standardized by the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) as MIL-STD-3005 in 1997 and superseded LPC-10 as the low bit rate DOD standard. Furthering the codec’s development, enhancements were incorporated into the MELP standard. As a result MELPe (Enhanced MELP (Multi-Excited-Linear-Prediction) was adopted in 2001 as the new standard. MELPe incorporates lower bit rates (1200 bps, and 600 bps) and includes a noise preprocessor (NPP) which is intended to reduce many types of background noise. Additionally MELPe’s decoder incorporates a postfilter to improve voice quality. MELPe was standardized across NATO platforms (STANAG 4591) in 2002.
DOD’s primary goal was to develop a digitally narrowband codec that could perform well in adversarial jamming conditions. Sampled at 8 kHz, MELPE achieves this by compressing digital speech to 2400 bps, 1200 bps or 600 bps.
Adaptive Digital's MELPe Codec
Adaptive Digital’s highly optimized MELPe voice compression codec supports the following platforms: Texas Instruments’ TMS320C6000, TMS320C5000 | Arm Architectures (v5, v6, v7-A/R, Armv7E-M, Armv8-A, Armv8-R) | Linux 32-bit/64-bit | Windows x86 / x64.
Adaptive Digital has optimized MELPe to run on the Xilinx MicroBlaze™ Soft Processor Core. A first in the industry, Adaptive Digital is opening new doors by giving our clients the opportunity to consider FPGAs as platforms for the codec requirements.
Features List
Functions are C-calleble
Multiple channel capable
Improved postfilter to enhance speech quality
- Optional noise preprocessing to reduce background noise
- Transcodes between rates
- Interoperable with the legacy MELP systems, enhancing speech quality of both ends
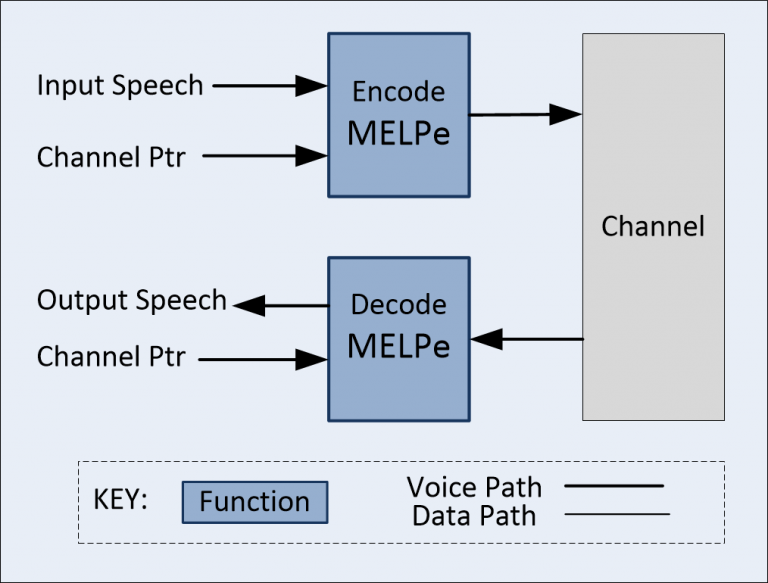
Coding Rates: 2400, 1200, and 600 bps
Sampling Rate: 8 kHz
FRAME SIZE
The MELPe coder frame size is dependent on the Encode/Decode rate
| Rate | Frame Size (Samples) | Frame Size (msec) |
| 600 bps | 720 | 90.0 |
| 1200 bps | 540 | 67.5 |
| 2400 bps | 180 | 22.5 |
Availability
| Platforms / Operating Systems / Core |
| Arm ® Devices – Armv7 Cortex-A5/A7/A8 / A9 / A15, | Cortex-M3 / M4 / M7 | Cortex-R5 | Legacy Arm9E/Arm11 |
| Arm ® Devices – Armv8-A Cortex-A53 / A57 | Cortex-A72 / A73 |
| Texas Instruments – TI TMS320C6000 C64x/C64x+, C674x, TMS320C5000 C55x / C54x |
| Windows x86 (32-bit) / x64 (64-bit) |
| Linux 32-bit / 64-bit |
| FPGA – Xilinx MicroBlaze 32-bit RISC Harvard architecture soft processor core |
ADT MELPe is available on the above Platforms: Other configurations are available upon request.
Specifications
MELPe Armv7 Cortex-A | Armv8 Cortex-A53
MEMORY REQUIREMENTSAll Memory usage is given in units of byte
| MIPS | MIPS (600bps) | MIPS (1200 bps) | MIPS (2400 bps) |
| Nonlinear Preprocessor (NPP) | 14 | 14 | 14 |
| Encoder | 46 | 44 | 27 |
| Decoder | 17 | 17 | 17 |
MEMORY REQUIREMENTS
All Memory usage is given in units of byte
| Cortex-A | Program | Channel | Tables | Data |
| Encoder | 192k | 6560 | 170k | 6k |
| Decoder | 1376 | |||
| NPP | 11968 |
MELPe Arm Cortex-M7
CPU UTILIZATION| MIPS | MIPS (600bps) | MIPS (1200 bps) | MIPS (2400 bps) |
| Nonlinear Preprocessor (NPP) | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Encoder | 32.4 | 31.2 | 25.8 |
| Decoder | 12.6 | 13.2 | 13.2 |
| Total | 60 | 59.4 | 54 |
MEMORY REQUIREMENTS
All Memory usage is given in units of byte
| Cortex-M7 | Program | Channel | Scratch | Tables | Data |
| Encoder | 100k | 6560 | 6984 | 148k | 63k |
| Decoder | 1376 | ||||
| NPP | 11968 |
MELPe Arm Cortex-M4 | Cortex-R5
CPU UTILIZATION| MIPS | MIPS (600bps) | MIPS (1200 bps) | MIPS (2400 bps) |
| Nonlinear Preprocessor (NPP) | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| Encoder | 54 | 52 | 43 |
| Decoder | 21 | 22 | 22 |
| Total | 100 | 99 | 90 |
MEMORY REQUIREMENTS
All Memory usage is given in units of byte
| Cortex-M4 | R5 | Program | Channel | Scratch | Tables | Data |
| Encoder | 100k | 6560 | 6984 | 148k | 63k |
| Decoder | 1376 | ||||
| NPP | 11968 |
MELPe Arm11/Arm9E
CPU UTILIZATION| MIPS | MIPS (600bps) | MIPS (1200 bps) | MIPS (2400 bps) |
| Nonlinear Preprocessor (NPP) | 35 | 35 | 35 |
| Encoder | 493 | 489 | 81 |
| Decoder | 27 | 27 | 27 |
TMS320C6000
MELPe C64x+ / C66x | OMAP C674
CPU UTILIZATION| MIPS | MIPS (600bps) | MIPS (1200 bps) | MIPS (2400 bps) |
| Nonlinear Preprocessor (NPP) | 11.4 | 11.5 | 13.7 |
| Encoder | 23.4 | 23.5 | 24.8 |
| Decoder | 15.1 | 15.1 | 17.4 |
MEMORY REQUIREMENTS
All Memory usage is given in units of byte
| C64x+ | Program | Channel | Scratch | Tables | Data |
| Encoder | 191k | 6560 | 6984 | 163k | 70k |
| Decoder | 1376 | ||||
| NPP | 11968 |
MELPe C64x
MEMORY REQUIREMENTSAll Memory usage is given in units of byte
| C64x | Program | Channel | Scratch | Tables | Data |
| Encoder | 188.4k | 6560 | 5672 | 148k | 63k |
| Decoder | 1376 | ||||
| NPP | 11968 |
MELPe C6416
CPU UTILIZATION| MIPS (C6416) | MIPS (600bps) | MIPS (1200 bps) | MIPS (2400 bps) |
| Nonlinear Preprocessor (NPP) | 12.2 | 12.2 | 13.3 |
| Encoder | 23.7 | 27.5 | 24.8 |
| Decoder | 15.7 | 22.5 | 17.4 |
TMS320C5000
MELPe C55x
CPU UTILIZATION| Software – MELPePlus | 600 bps | 600 bps | 1200 bps | 1200 bps | 2400 bps | 2400 bps |
| Max | Average | Max | Average | Max | Average | |
| Encode | 34.2 | 32.5 | 46.5 | 41.3 | 29.7 | 26.6 |
| Decode | 12.7 | 10.7 | 14.4 | 11.2 | 14.8 | 13.3 |
| Noise Preprocessor (NPP) | 19.6 | 18.7 | 20 | 19 | 21.8 | 20.5 |
MEMORY REQUIREMENTS
All Memory usage is given in units of byte
| C55x | Program | Channel | Scratch | Tables | Data |
| Encoder | 78.3k | 6560 | 6984 | 162k | 5k |
| Decoder | 1600 | ||||
| NPP | 11968 |
MELPe Linux (32-bit)*
CPU UTILIZATION*Contact sales for 64-bit specifications.
| MIPS | MIPS (600bps) | MIPS (1200 bps) | MIPS (2400 bps) |
| Nonlinear Preprocessor (NPP) | 76 | 78 | 78 |
| Encoder | 214 | 238 | 207 |
| Decoder | 71 | 71 | 71 |
MELPe Windows x86 (32-bit)*
CPU UTILIZATION*Contact sales for 64-bit specifications.
| MIPS | MIPS (600bps) | MIPS (1200 bps) | MIPS (2400 bps) |
| Nonlinear Preprocessor (NPP) | 84 | 83 | 85 |
| Encoder | 250 | 279 | 237 |
| Decoder | 70 | 68 | 72 |
MELPe Xilinx | MicroBlaze
CPU UTILIZATION| MIPS MicroBlaze | MIPS (600bps) | MIPS (1200 bps) | MIPS (2400 bps) | |||
| Function | Peak | Avg | Peak | Avg | Peak | Avg |
| Nonlinear Preprocessor (NPP) | 28 | 26 | 28 | 26 | 28 | 26 |
| Encoder | 113 | 109 | 116 | 97 | 96 | 84 |
| Decoder | 39 | 36 | 42 | 36 | 52 | 37 |
| Total | 178 | 171 | 180 | 159 | 176 | 150 |
MEMORY REQUIREMENTS
All Memory usage is given in units of byte.
| MicroBlaze | Program | Channel | Scratch | Tables | Data |
| Encoder | 349k | 6560 | 7000 | 820 | 377k |
| Decoder | 1376 | ||||
| NPP | 11968 |
Description
The MELP Vocoder uses a mixed-excitation model that can produce more natural sounding speech because it can represent a richer ensemble of possible speech characteristics. The MELPe enhanced speech coders’ quality surpasses that of the original MELP vocoder. The MELPe software is capable of running multi streams (multi-channel) together, either encoding and decoding concurrently.
The MELPe codec supports three different vocoder bitrates: 2400, 1200, and 600 bps. The basic 2400 bps bitrate vocoder uses a 22.5 ms frame of speech consisting of 180 8000-Hz, 16-bit speech samples. The 1200 and 600 bps bitrate vocoders each use three and four 22.5 ms frames of speech, respectively.
These reduced-bitrate vocoders internally use multiple 2400 bps parameter sets with further processing to strategically remove redundancy. The payload sizes for each of the bitrates are 54, 81, and 54 bits for the 2400, 1200, and 600 bps frames, respectively.
The MELPe algorithm distinguishes between voiced and unvoiced speech and encodes each differently. Unvoiced speech can be coded with fewer information bits for the same quality.
Commercial applications have arisen because of the low-bitrate property of MELPe with its (relatively) high intelligibility. Because of this, MELPe is being used in a variety of wired and radio communications systems.
Function API's
API function call summary
MELPE_ADT_initEncode (…) Initializes the MELPe encoder
MELPE_ADT_initDecode (…) Initializes the MELPe decoder
MELPE_ADT_encode (…) Executes the MELPe encoder
MELPE_ADT_decode (…) Executes the MELPe decoder
NPP_ADT_init (…) Initializes the Melpe noise pre-processor
NPP_ADT_process (…) Executes the Melpe noise pre-processor
